本文共 8774 字,大约阅读时间需要 29 分钟。
文章目录
SDS
结构分析
由于C字符串存在大量问题,所以在Redis中,并没有使用C风格字符串,而是自己构建了一个简单动态字符串即SDS(simple dynamic string)
struct sdshdr { // buf 中已占用空间的长度 int len; // buf 中剩余可用空间的长度 int free; // 数据空间 char buf[];}; 为解决C字符串缓冲区溢出问题以及长度计算问题,SDS中引入了len来统计当前已使用空间长度,free来计算剩余的空间长度
C字符串的主要缺陷就是因为它没有记录自己的长度,而如果在需要了解长度时,就只能通过O(N)的效率进行一次遍历

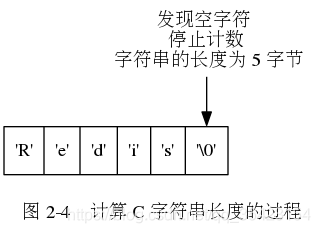
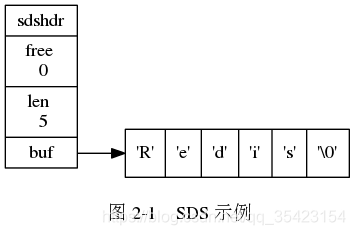 通过标记剩余空间,当对SDS进行插入操作时,就会提前判断当前剩余空间是否足够,如果不足则会先进行空间的拓展,再进行插入,这样就解决了缓冲区溢出的问题
通过标记剩余空间,当对SDS进行插入操作时,就会提前判断当前剩余空间是否足够,如果不足则会先进行空间的拓展,再进行插入,这样就解决了缓冲区溢出的问题 内存策略
由于Redis作为一个高效的内存数据库,用于速度要求严苛,插入删除频繁
的场景,为了提高内存分配的效率,防止大量使用内存重分配而调用系统函数导致的性能损失问题(用户态和内核态的切换),Redis主要依靠空间预分配和惰性空间释放来解决这个问题空间预分配
为减少空间分配的次数,当需要进行空间拓展时,不仅仅会为SDS分配修改所必须要的空间,并且会为SDS预分配额外的未使用空间。
预分配未使用空间的策略如下
- 当SDS修改后的长度小于1MB时,将会预分配大小和当前len一样的空间(free = len),也就是使空间增长一倍,来减少因为初始时申请大空间导致的连续分配问题
- 当SDS修改后的长度大于等于1MB时,每次分配都会分配1MB的空间,防止空间的浪费。
惰性空间释放
当我们对SDS进行删除操作时,并不会立即回收删除后空余的空间,而是将空余空间以free字段记录下来,以备后面使用。
这样做的目的在于防止因为空间缩短后因为再度插入导致的空间拓展问题。 并且如果有需求需要真正释放空间,Redis也提供了对应的API,所以不必担心会因为惰性的空间释放而导致的内存浪费问题。总结
比起 C 字符串, SDS 具有以下优点:
- 常数复杂度获取字符串长度。(len字段)
- 杜绝缓冲区溢出。(free字段)
- 减少修改字符串长度时所需的内存重分配次数。(空间预分配,惰性空间释放)
- 二进制安全。(以二进制形式处理)
- 兼容部分 C 字符串函数。(底层基于C字符串,以空字符结尾)
链表
结构分析
typedef struct listNode { // 前置节点 struct listNode *prev; // 后置节点 struct listNode *next; // 节点的值 void *value;} listNode;/* * 双端链表迭代器 */typedef struct listIter { // 当前迭代到的节点 listNode *next; // 迭代的方向 int direction;} listIter;/* * 双端链表结构 */typedef struct list { // 表头节点 listNode *head; // 表尾节点 listNode *tail; // 节点值复制函数 void *(*dup)(void *ptr); // 节点值释放函数 void (*free)(void *ptr); // 节点值对比函数 int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key); // 链表所包含的节点数量 unsigned long len;} list; 

同时为了实现多态与泛型,链表中还提供了dup,free,match属性来设置相关的函数,使得链表支持不同类型的值的存储
总结
- 链表被广泛用于实现 Redis 的各种功能, 比如列表键, 发布与订阅, 慢查询, 监视器, 等等。
- 每个链表节点由一个 listNode 结构来表示, 每个节点都有一个指向前置节点和后置节点的指针, 所以 Redis 的链表实现是双端链表。
- 每个链表使用一个 list 结构来表示, 这个结构带有表头节点指针、表尾节点指针、以及链表长度等信息。
- 因为链表表头节点的前置节点和表尾节点的后置节点都指向 NULL , 所以 Redis 的链表实现是无环链表。
- 通过为链表设置不同的类型特定函数, Redis 的链表可以用于保存各种不同类型的值。
字典
结构分析
Redis的字典底层采用了哈希表来进行实现。
首先看看字典底层哈希表的结构
typedef struct dictht { // 哈希表数组 dictEntry **table; // 哈希表大小 unsigned long size; // 哈希表大小掩码,用于计算索引值 // 总是等于 size - 1 unsigned long sizemask; // 该哈希表已有节点的数量 unsigned long used;} dictht; 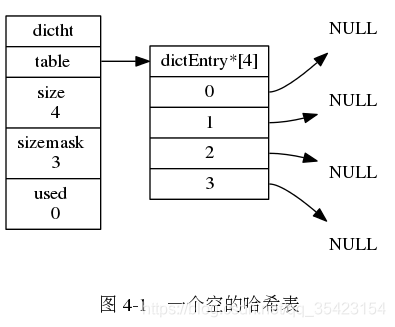
为解决哈希冲突,Redis字典采用了链地址法来构造了哈希桶的结构,也就是哈希数组中的每个元素都是一个链表。

下面来看看哈希节点的结构
typedef struct dictEntry { // 键 void *key; // 值 union { void *val; uint64_t u64; int64_t s64; } v; // 指向下个哈希表节点,形成链表 struct dictEntry *next;} dictEntry; 可以看到,为保证键值对适用于多重类型,key值使用的时void的形式,而value使用了64位有符号整型和64位无符号整型,void指针的一个联合体,每个节点使用next来链接成一个链表
typedef struct dictType { // 计算哈希值的函数 unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key); // 复制键的函数 void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key); // 复制值的函数 void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj); // 对比键的函数 int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2); // 销毁键的函数 void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key); // 销毁值的函数 void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);} dictType; 为保证字典具有多态及泛型,dictType中提供了如哈希函数以及K-V的各种操作函数,使得字典适用于多重情景
rehash
/* * 字典 */typedef struct dict { // 类型特定函数 dictType *type; // 私有数据 void *privdata; // 哈希表 dictht ht[2]; // rehash 索引 // 当 rehash 不在进行时,值为 -1 int rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */ // 目前正在运行的安全迭代器的数量 int iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */} dict; 从字典的结构中,我们可以看到里面同时存放了两个哈希表,以及一个rehashidx属性。
这就牵扯到了字典的核心之一,rehash。Redis作为一个插入频繁且对效率要求高的数据库,当插入的数据过多时,就会因为哈希表中的负载因子过高而导致查询或者插入的效率降低,此时就需要通过rehash来进行重新扩容并重新映射。
但是如果只是用一个哈希表,映射时就会导致数据库暂时不可用,作为一个使用频繁的数据库,短期的停机几乎是不可容许的问题,所以Redis设计时采用了双哈希的结构,并采用了渐进式rehash的方法来解决这个问题。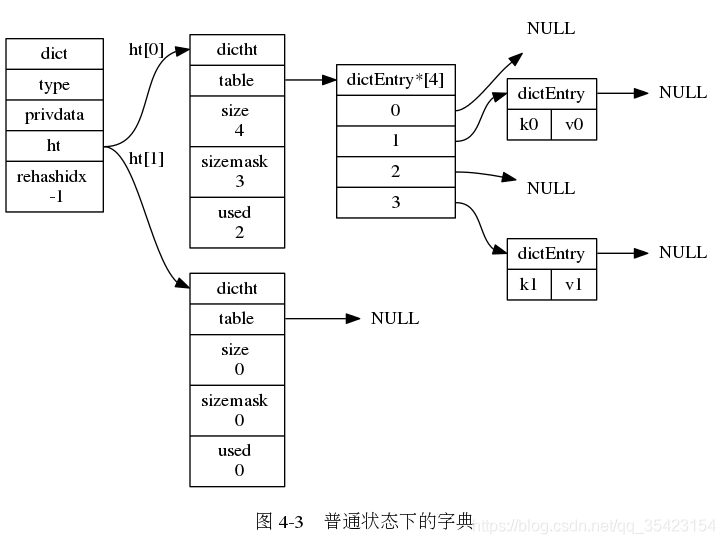
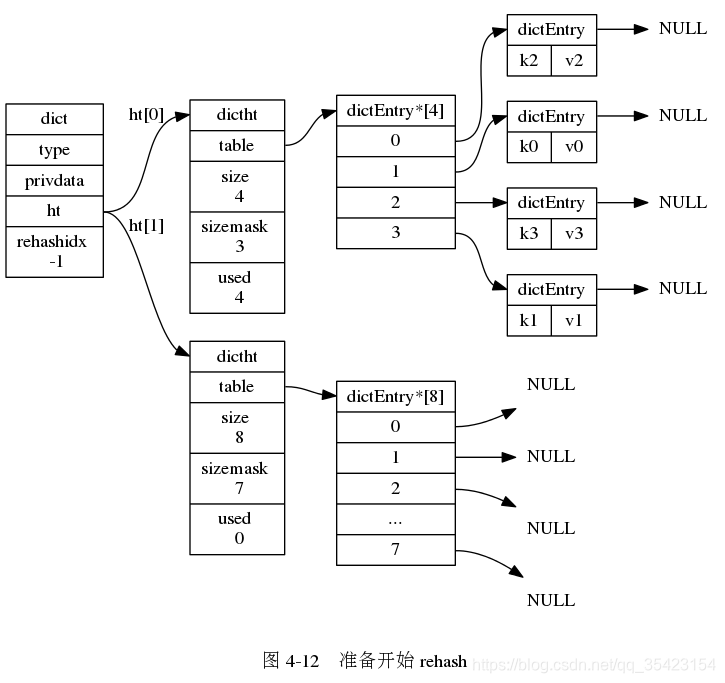
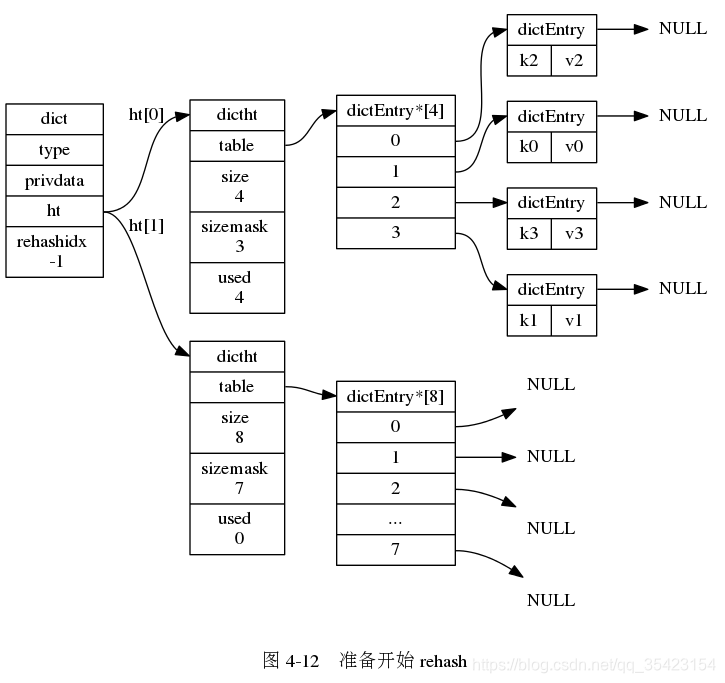
rehash的步骤如下
- 为ht[1]的哈希表分配空间
- 将ht[0]中的键值对重新映射到ht[1]上
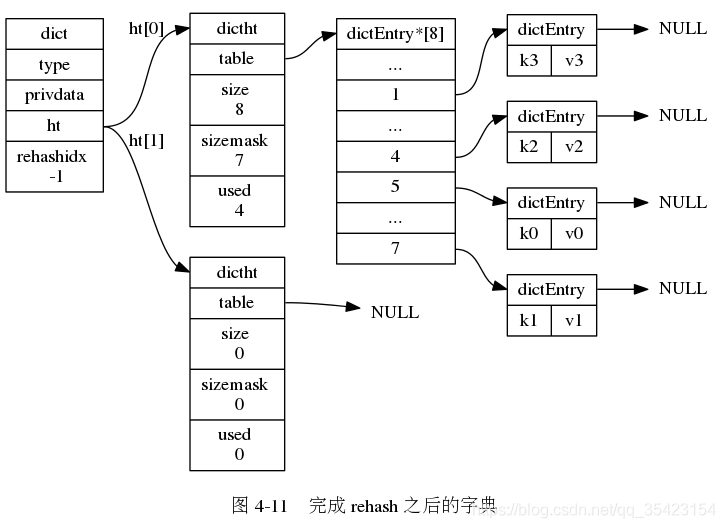
- 当ht[0]的数据迁移完成,此时ht[0]为一个空表,此时释放ht[0],并让ht[1]成为新的ht[0],再为ht[1]创建一个新的空白哈希表,为下一次的rehash做准备

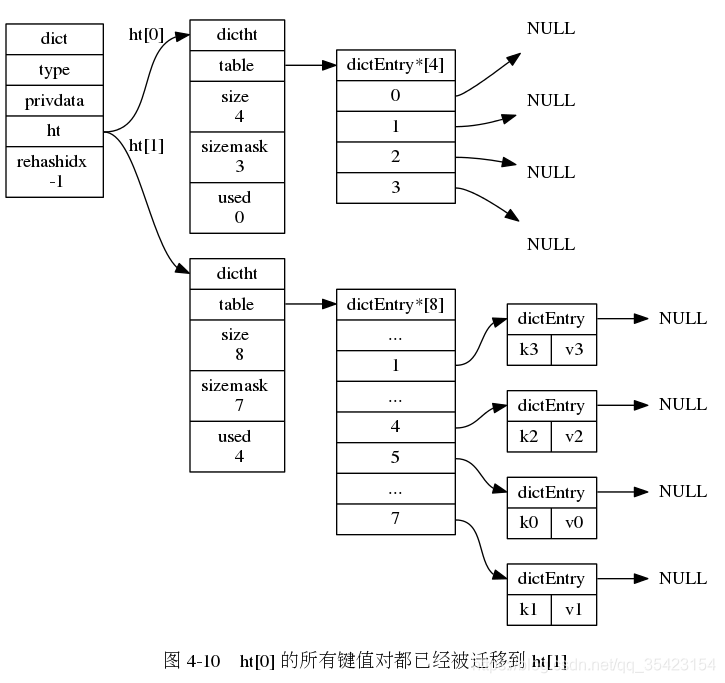
渐进式rehash
由于数据库中可能存在大量的数据,而rehash的时候又过长,为了避免因为rehash造成的服务器停机,rehash的过程并不是一次完成的,而是一个多次的,渐进式的过程。
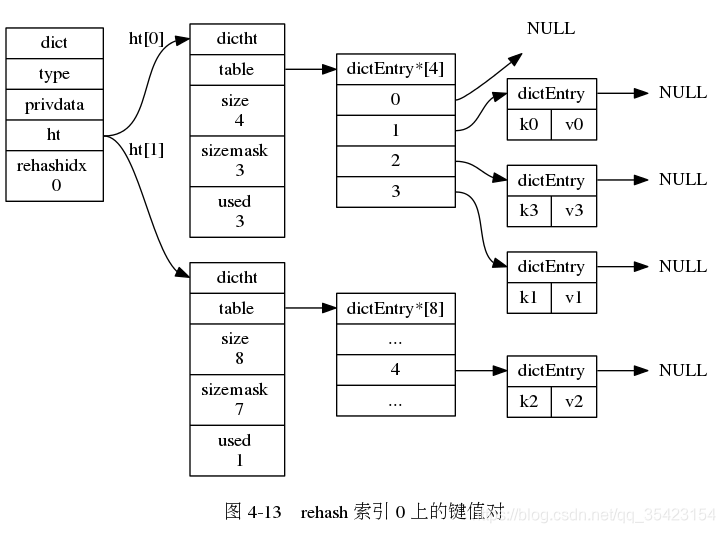
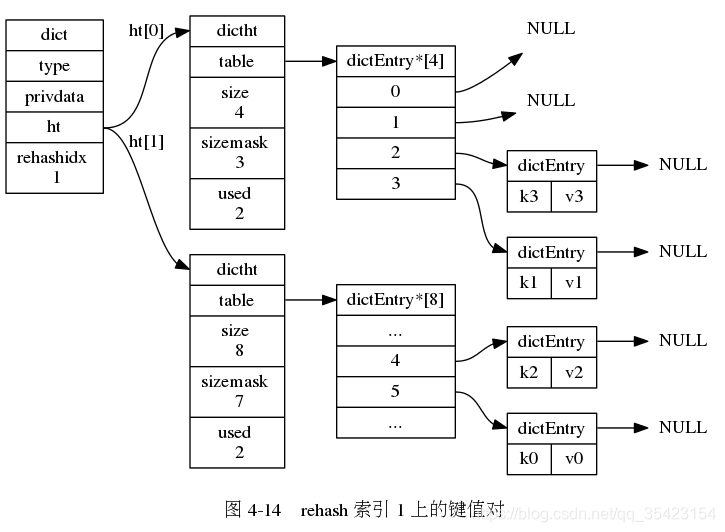
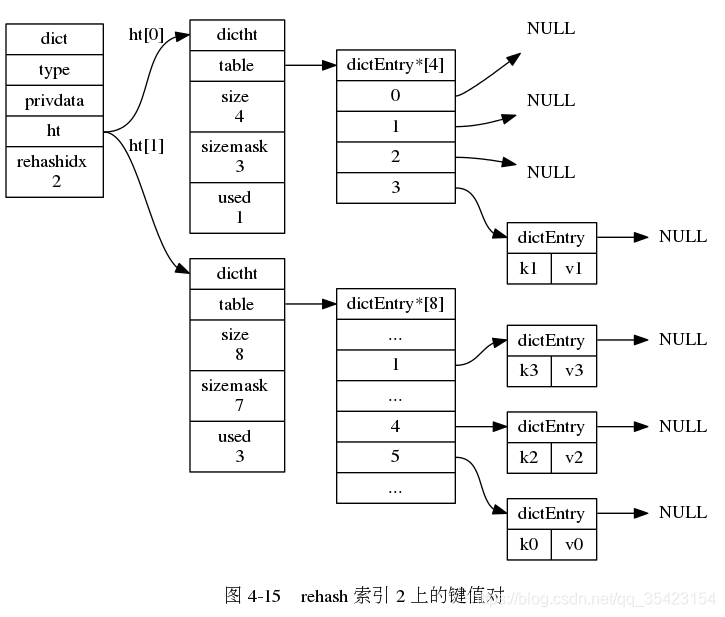
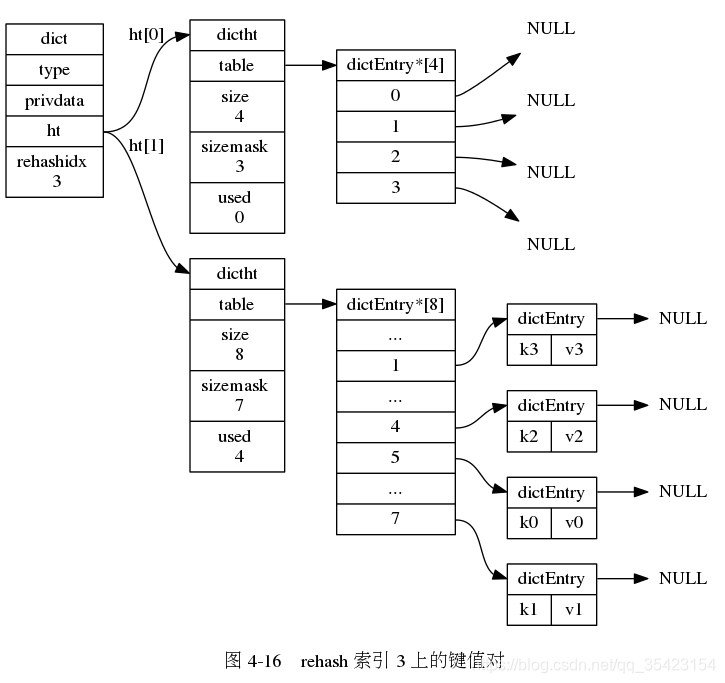
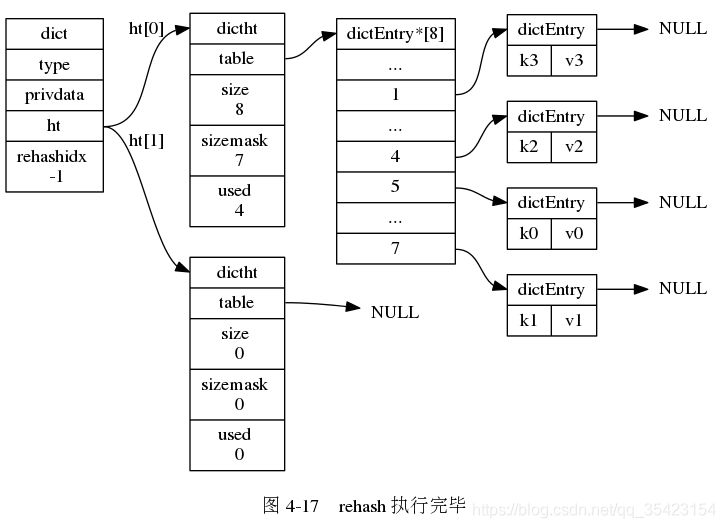 在渐进式rehash的时候,由于数据不断的进行迁移,无法确定数据处于哪一个表上, 此时如果进行插入、删除、查找的操作时就会在两个表上进行,如果在一个表中没找到对应数据,就会到另一个表中继续查找。
在渐进式rehash的时候,由于数据不断的进行迁移,无法确定数据处于哪一个表上, 此时如果进行插入、删除、查找的操作时就会在两个表上进行,如果在一个表中没找到对应数据,就会到另一个表中继续查找。 并且如果此时新插入节点,都会统一的防止在新表ht[1]中,防止对ht[0]的rehash造成干扰,保证ht[0]节点的只减少不增加
总结
- 字典被广泛用于实现 Redis 的各种功能, 其中包括数据库和哈希键。
- Redis 中的字典使用哈希表作为底层实现, 每个字典带有两个哈希表, 一个用于平时使用, 另一个仅在进行 rehash 时使用。
- 当字典被用作数据库的底层实现, 或者哈希键的底层实现时, Redis 使用 MurmurHash2 算法来计算键的哈希值。
- 哈希表使用链地址法来解决键冲突, 被分配到同一个索引上的多个键值对会连接成一个单向链表。
- 在对哈希表进行扩展或者收缩操作时, 程序需要将现有哈希表包含的所有键值对 rehash 到新哈希表里面, 并且这个 rehash 过程并不是一次性地完成的, 而是渐进式地完成的。
跳表
跳表是一个较为少见的数据结构,如果不了解的可以看看我之前的博客
由于跳表的实现简单且性能可与平衡树相媲美,对于大量插入删除的数据库来说,跳表只需要进行简单的链表插入和索引的选拔,而不像平衡树一样需要进行整体平衡的维持。并且由于在范围查找上的效率远远强于平衡树,所以Redis底层选取跳表来作为有序集合的底层之一。结构分析
typedef struct zskiplistNode { // 成员对象 robj *obj; // 分值 double score; // 后退指针 struct zskiplistNode *backward; // 层 struct zskiplistLevel { // 前进指针 struct zskiplistNode *forward; // 跨度 unsigned int span; } level[];} zskiplistNode; 跳跃表的查询从最顶层出发,通过前进指针来往后查找,通过比较节点的分数来判断当前节点是否与索引匹配,如果查找不到则进入下层继续查找,并记录下跨越的层数span来进行排位。
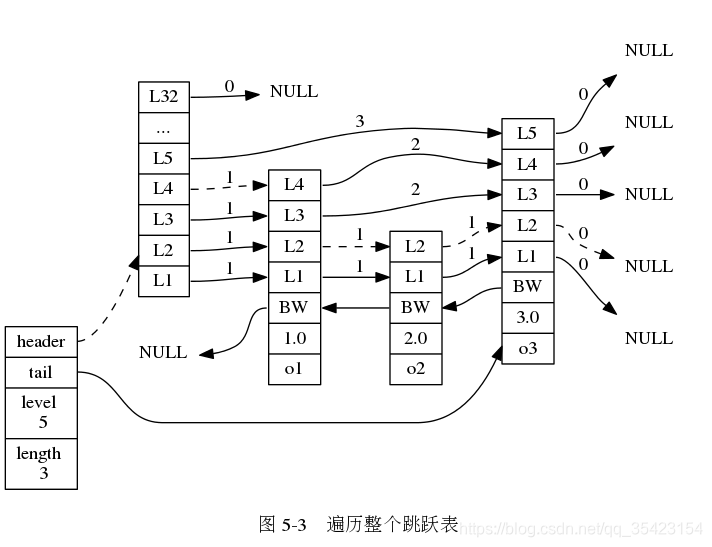 同时为了处理特殊情况,还准备了一个后退指针来进行从表尾到表头的遍历,但是与前进不同,后退指针并不存在跳跃,而是只能一个一个向后查询
同时为了处理特殊情况,还准备了一个后退指针来进行从表尾到表头的遍历,但是与前进不同,后退指针并不存在跳跃,而是只能一个一个向后查询 
/* * 跳跃表 */typedef struct zskiplist { // 表头节点和表尾节点 struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail; // 表中节点的数量 unsigned long length; // 表中层数最大的节点的层数 int level; } zskiplist; 跳跃表通过保存表头和表尾节点,来快速访问表头和表尾。并且保存了节点的数量来实现O(1)的长度计算
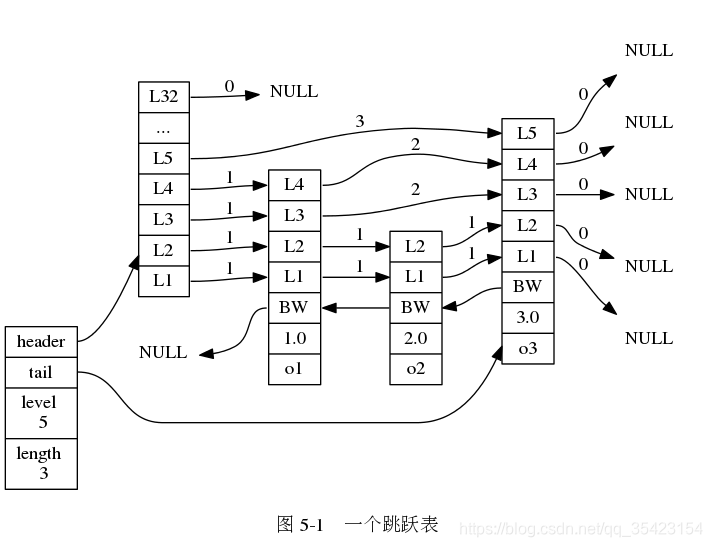 为了避免因为层数过高导致的大量空间损失,Redis跳跃表的节点高度最高位32层。
为了避免因为层数过高导致的大量空间损失,Redis跳跃表的节点高度最高位32层。 总结
- 跳跃表是有序集合的底层实现之一, 除此之外它在 Redis 中没有其他应用。
- Redis 的跳跃表实现由 zskiplist 和 zskiplistNode 两个结构组成, 其中 zskiplist 用于保存跳跃表信息(比如表头节点、表尾节点、长度), 而 zskiplistNode 则用于表示跳跃表节点。
- 每个跳跃表节点的层高都是 1 至 32 之间的随机数。
- 在同一个跳跃表中, 多个节点可以包含相同的分值, 但每个节点的成员对象必须是唯一的。
- 跳跃表中的节点按照分值大小进行排序, 当分值相同时, 节点按照成员对象的大小进行排序。
整数集合
整数集合时集合键的底层实现之一,当集合中的元素全部都是整数值的时候,并且集合中元素不多时,Redis就会使用整数集合来作为集合键的底层结构。整数集合具有去重且排序的特性
结构分析
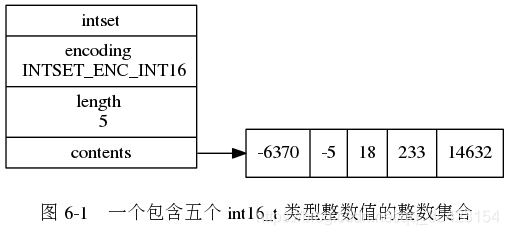
typedef struct intset { // 编码方式 uint32_t encoding; // 集合包含的元素数量 uint32_t length; // 保存元素的数组 int8_t contents[];} intset; 在上面的结构中,虽然content数组的类型是一个8bit的整型,但是数据真正存储的方式并不是这个类型,而是根据encoding来决定具体的类型,8bit只是作为一个基本单位来进行使用。
例如此时encoding设置为INTSET_ENC_INT16时,数组存储的格式就有每个元素16bit
 如果encoding设置为INTSET_ENC_INT64时,数组存储的格式就有每个元素64bit
如果encoding设置为INTSET_ENC_INT64时,数组存储的格式就有每个元素64bit 
升级
升级的流程
- 根据插入的类型来决定集合升级的类型,拓展数组的整体空间并为新节点分配空间
- 对集合中所有数据类型进行升级,在保持有序的前提下将所有升级后的元素移动到合适的位置上
- 将新节点插入到集合的对应位置
新元素的插入位置
由于会引起升级的元素的类型都必顶比数组中的所有数据都大,所以也就决定了其要么比所有数据都大,要么比所有数据都小(负数),所以插入位置只能是首部和尾部- 当新元素比所有数据都大时在尾部插入
- 当新元素比所有数据都小时在首部插入

 如果插入一个32位的数据,则引起全体升级
如果插入一个32位的数据,则引起全体升级  分配底层空间
分配底层空间 
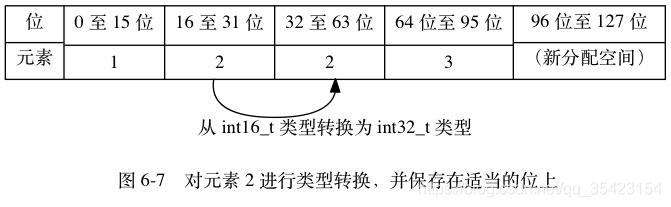 整体升级并挪动位置
整体升级并挪动位置 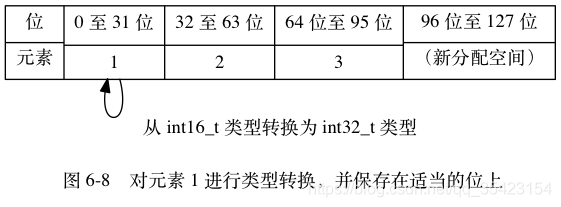
插入元素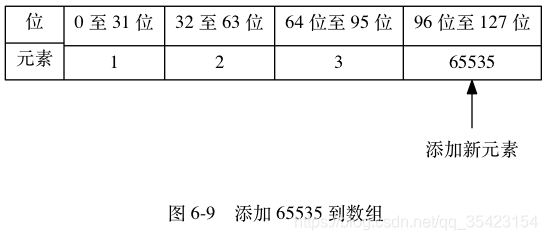
降级
在整数列表中升级是一个不可逆的过程,即使将所有高类型的数据删除了,也不会进行降级。
理由是防止因为降级后再次升级带来的大量数据挪动的问题,在保证了效率的同时,也带来了一定程度上的空间浪费(非必要时尽量不要升级)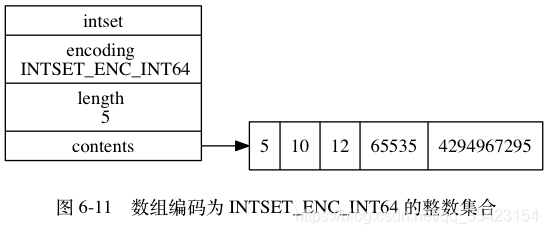
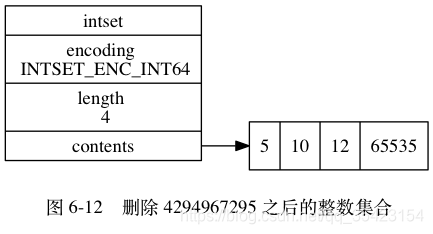 升级带来的好处
升级带来的好处 - 灵活 : 由于C语言是一个静态类型语言,为了避免出现类型错误通常会将不同类型分开,例如如果要存储16bit、32bit、64bit的整型就需要3个数组,但是使用整数集合就可以通过升级的策略来进行元素类型的自适应,就可以任意的将各种类型的整数插入进去,而不必担心类型错误
- 节约内存:与上面类似,如果我们只有一个64bit的数组,而里面存储了不少16bit、32bit的元素,则会造成空间的大量浪费。而使用整数集合则可以同时保存多个类型,只需要确保升级的操作只在必要时进行,就不会造成空间的浪费
总结
- 整数集合是集合键的底层实现之一。
- 整数集合的底层实现为数组, 这个数组以有序、无重复的方式保存集合元素, 在有需要时, 程序会根据新添加元素的类型, 改变这个数组的类型。
- 升级操作为整数集合带来了操作上的灵活性, 并且尽可能地节约了内存。
- 整数集合只支持升级操作, 不支持降级操作。
压缩列表
压缩列表(ziplist)是列表键和哈希键的底层实现之一。
当一个列表键只包含少量列表项, 并且每个列表项要么就是小整数值, 要么就是长度比较短的字符串, 那么 Redis 就会使用压缩列表来做列表键的底层实现。主要核心就是为了节约空间
结构分析

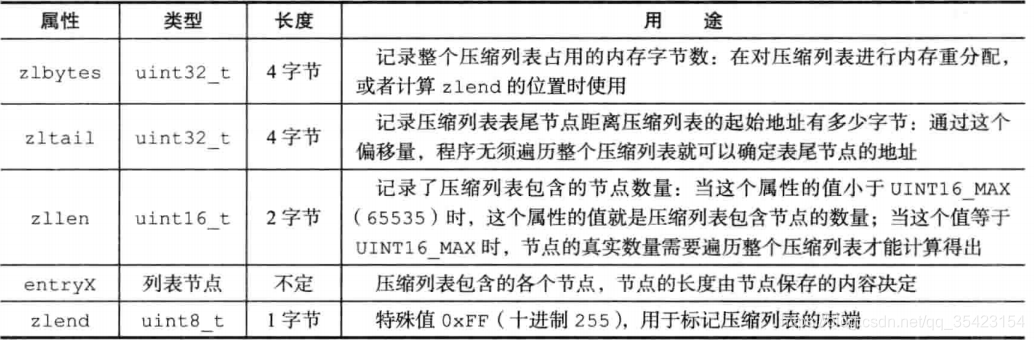
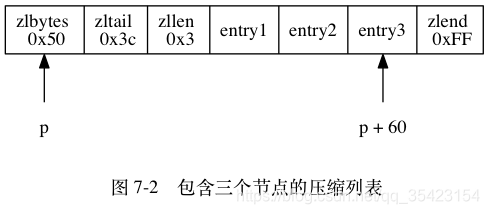 例如这张图,可以看出当前包含三个节点,总空间为0x50(十进制80),到尾部的偏移量为0x3c(十进制60),节点数量为0x3(十进制3)
例如这张图,可以看出当前包含三个节点,总空间为0x50(十进制80),到尾部的偏移量为0x3c(十进制60),节点数量为0x3(十进制3) 
整数的类型可以是以下六种之一:
- 4位的介于0-12的无符号整数
- 1字节的有符号整数
- 3字节的有符号整数
- int16_t
- int32_t
- int64_t
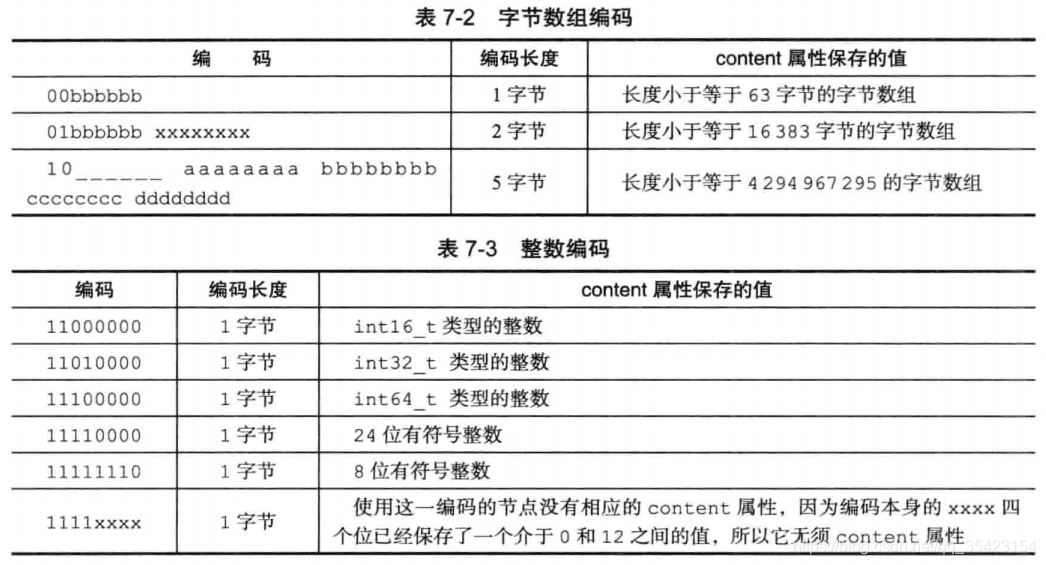
字节数组可以是以下三种之一:
- 长度小于等于63(2^6 -1)字节的字节数组
- 长度小于等于16383(2^14 -1)字节的字节数组
- 长度小于等于4294967295(2^32 -1)字节的字节数组
而压缩列表节点又有三个属性组成,分别是previous_entry_length,encoding,content。
previous_entry_length
这个属性记录了压缩列表前一个节点的长度,该属性根据前一个节点的大小不同可以是1个字节或者5个字节。- 如果前一个节点的长度小于254个字节,那么previous_entry_length的大小为1个字节,即前一个节点的长度可以使用1个字节表示
- 如果前一个节点的长度大于等于254个字节,那么previous_entry_length的大小为5个字节,第一个字节会被设置为0xFE(十进制的254),之后的四个字节则用于保存前一个节点的长度。
小于254字节时的表示
 大于等于254字节时的表示
大于等于254字节时的表示  为什么要这样设计呢? 由于压缩列表中的数据以一种不规则的方式进行紧邻,无法通过后退指针来找到上一个元素,而通过保存上一个节点的长度,用当前的地址减去这个长度,就可以很容易的获取到了上一个节点的位置,通过一个一个节点向前回溯,来达到从表尾往表头遍历的操作
为什么要这样设计呢? 由于压缩列表中的数据以一种不规则的方式进行紧邻,无法通过后退指针来找到上一个元素,而通过保存上一个节点的长度,用当前的地址减去这个长度,就可以很容易的获取到了上一个节点的位置,通过一个一个节点向前回溯,来达到从表尾往表头遍历的操作 encoding
encoding通过以下规则来记录content的类型- 一字节、两字节或者五字节长, 值的最高位为 00 、 01 或者 10 的是字节数组编码: 这种编码表示节点的 content 属性保存着字节数组, 数组的长度由编码除去最高两位之后的其他位记录;
- 一字节长, 值的最高位以 11 开头的是整数编码: 这种编码表示节点的 content 属性保存着整数值, 整数值的类型和长度由编码除去最高两位之后的其他位记录;
content
content属性负责保存节点的值,值的具体类型由上一个字段encoding来决定。例如存储字节数组,00表示类型为字节数组,01011表示长度为11
 存储整数值,表示存储的为整数,类型为int16_t
存储整数值,表示存储的为整数,类型为int16_t 
连锁更新
当添加或删除节点时,可能就会因为previous_entry_length的变化导致发生连锁的更新操作。
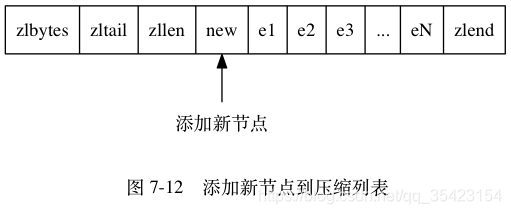
 但是问题来了,假设e1原本的大小为252字节,当previous_entry_length更新后它的大小则超过了254,此时又会引发对e2的更新。 顺着这个思路,一直更新下去
但是问题来了,假设e1原本的大小为252字节,当previous_entry_length更新后它的大小则超过了254,此时又会引发对e2的更新。 顺着这个思路,一直更新下去 
 同理,删除也会引发连锁的更新
同理,删除也会引发连锁的更新 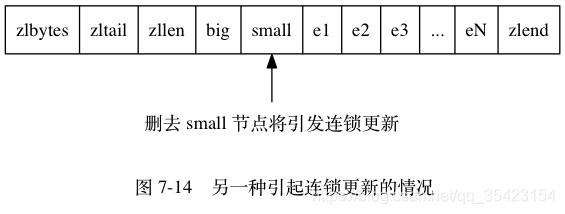 从上图可以看出来,在最坏情况下,会从插入位置一直连锁更新到末尾,即执行了N次空间重分配, 而每次空间重分配的最坏复杂度为 O(N) , 所以连锁更新的最坏复杂度为 O(N^2) 。
从上图可以看出来,在最坏情况下,会从插入位置一直连锁更新到末尾,即执行了N次空间重分配, 而每次空间重分配的最坏复杂度为 O(N) , 所以连锁更新的最坏复杂度为 O(N^2) 。 即使存在这种情况,但是并不影响我们使用压缩列表
- 压缩列表里要恰好有多个连续的、长度介于 250 字节至 253 字节之间的节点, 连锁更新才有可能被引发, 这种情况就和连中彩票一样,很少见
- 即使出现连锁更新, 但只要被更新的节点数量不多, 就不会对性能造成任何影响: 比如说, 对三五个节点进行连锁更新是绝对不会影响性能的;
总结
- 压缩列表是一种为节约内存而开发的顺序型数据结构。
- 压缩列表被用作列表键和哈希键的底层实现之一。
- 压缩列表可以包含多个节点,每个节点可以保存一个字节数组或者整数值。
- 添加新节点到压缩列表, 或者从压缩列表中删除节点, 可能会引发连锁更新操作, 但这种操作出现的几率并不高。
转载地址:http://gfmsz.baihongyu.com/